100% Pass Cisco, PMP, CISA, CISM, AWS Dumps on SALE!
Get Now
01:59:56
X
How to choose the network topology model when designing the network?
The topology of the network largely determines the performance of the network. Common network topologies mainly include star structure, mesh structure, ring structure, double plane, etc., which can be applied to the construction of most WANs, and at the same time, it is also applicable to the construction of most LANs. Different topologies have different characteristics, and the choice of topology in network construction depends on the actual situation.
1. Single star network
As shown in Figure 1, it can be suitable for small and medium-sized networks
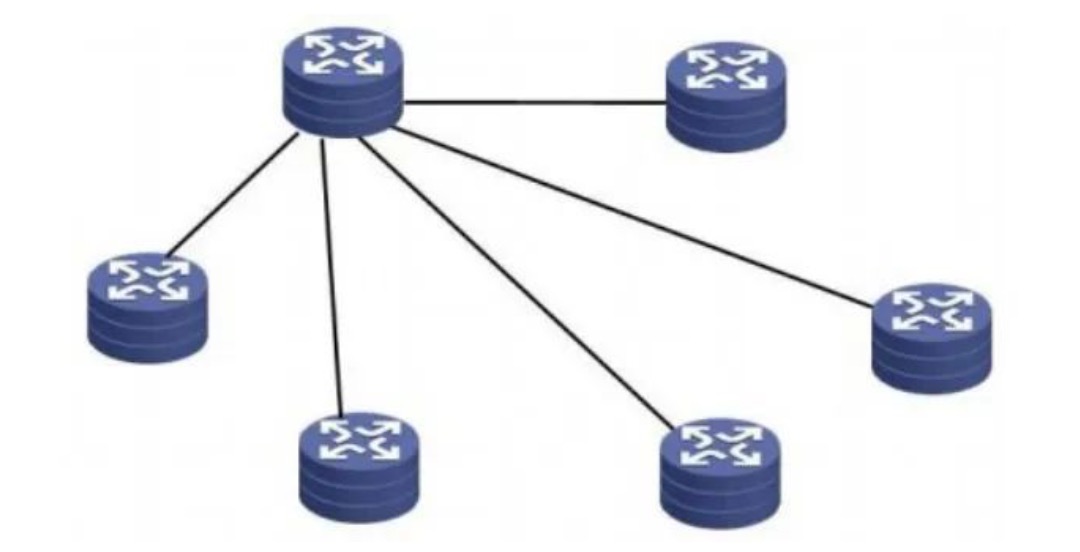
Has the following characteristics:
• Simple structure, easy to design;
• The line cost is relatively low;
• Good network scalability.
Disadvantages:
The processing capacity and interface bandwidth of the core device are very high. Once the core device fails, other nodes may not be able to communicate, and there is a single point of failure.
2. Double star structure
For a relatively large-scale network, there are many main branch nodes, and the double-star structure can be considered. as shown in picture 2,
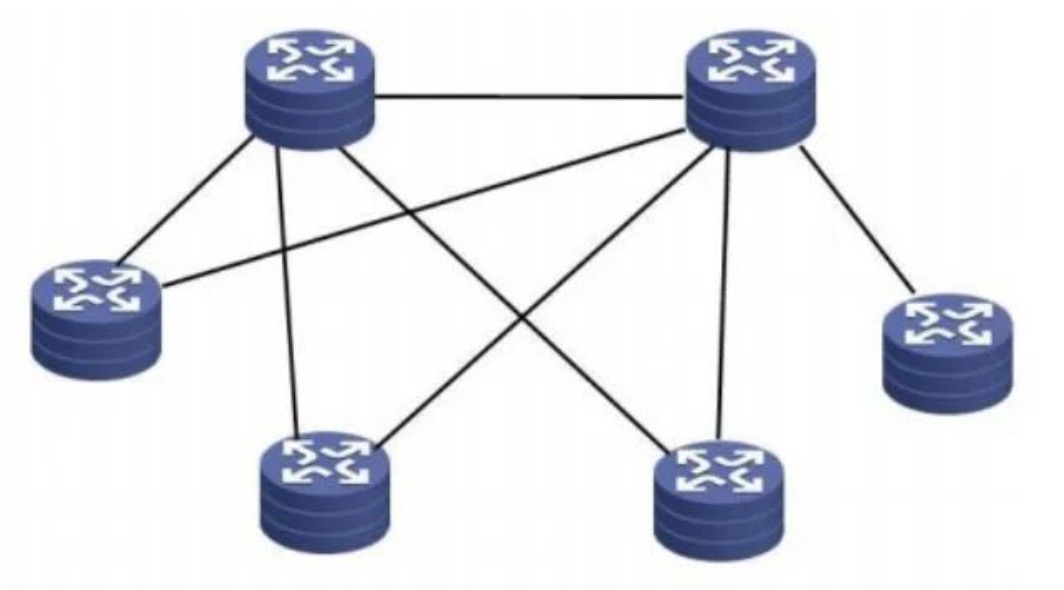
Has the following characteristics:
• High reliability.
• The dual-connected star network structure with two core nodes makes the network reliable, available, and secure, and avoids the hidden danger of single-point failure.
• Support traffic load sharing.
Network traffic may grow stronger with the development of multiple services (such as voice and video conferencing). The load sharing problem of network traffic will become the main factor of network availability. The use of a dual-connected network structure makes the network traffic more reasonable Distributed on each link.
Support network redundancy backup. The core node uses two high-performance network equipment, which makes the core layer have better redundancy backup capabilities. At the same time, high-speed link interconnection is required between the two core devices, which provides high-speed interconnection bandwidth between the core devices and avoids the transmission bottleneck between the two devices.
The double star structure is one of the network structures commonly used in actual networks.
1. Full mesh structure
For a relatively small-scale network, you can consider using a mesh structure. As shown in Figure 3:
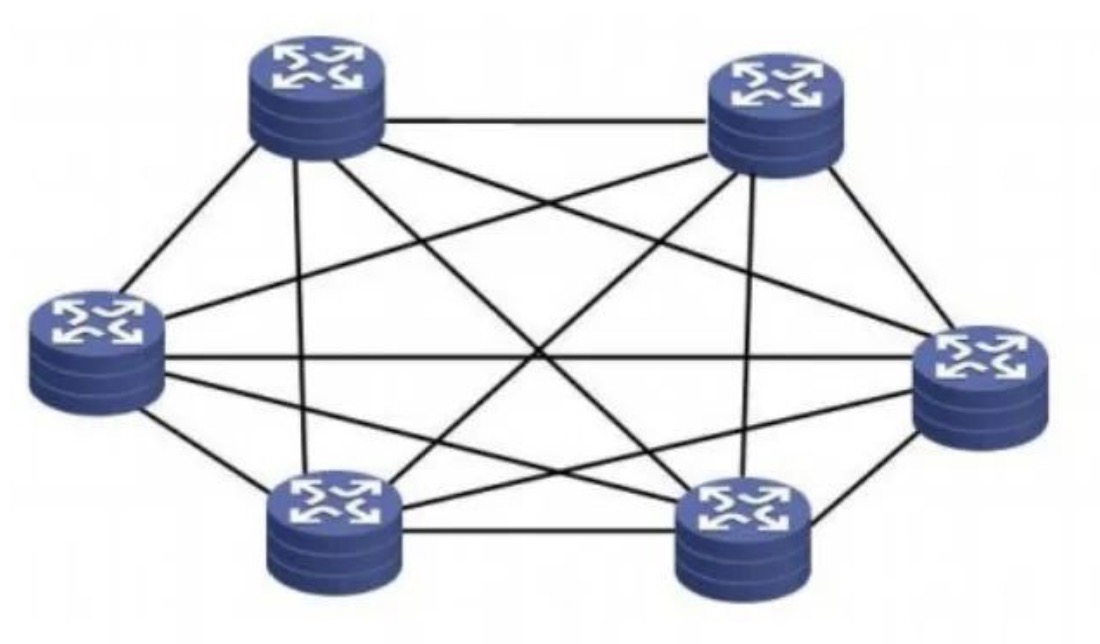
Has the following characteristics:
• Full meshed full connection between backbone routers, any two devices have a link connection, suitable for small networks with few backbone nodes.
• Provides a variety of alternative routes for communication between two points. It has the characteristics of high reliability and strong survivability, and there is no link bottleneck problem and failure problem.
• When there are many core devices, planning and deployment are more complicated.
2. Part of the mesh structure
Part of the mesh structure is to avoid a fully meshed N-level link in the case of multiple devices. According to the actual situation, you can choose to establish link connections between key nodes and other nodes, and selectively connect non-key nodes, such as Figure 4 shows:
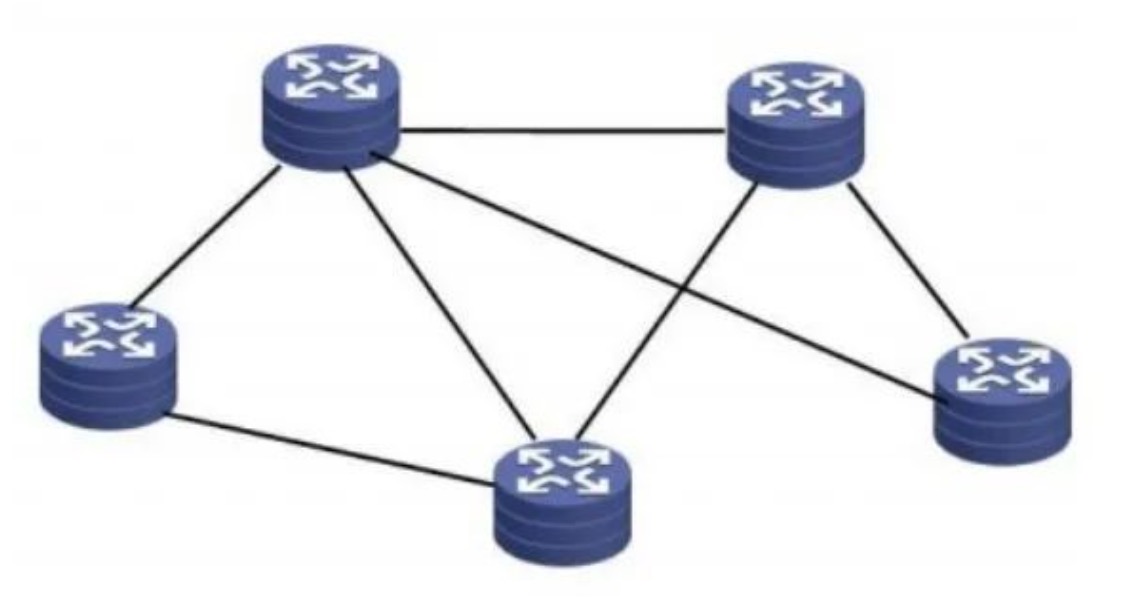
Part of the mesh structure partially solves the problems of the entire mesh, mainly the scalability problem, so it is more suitable for relatively large-scale networks.
Ring network
A ring network is formed by a number of nodes in the network, connected end to end by a point-to-point link to form a closed ring. This structure enables data to be transmitted between nodes in one direction in the ring, and information is transmitted from one node to another One node simplifies path selection. In the backbone and access network of the metropolitan area network, in the decentralized government network, enterprise network and campus network, ring networks can be used.
As shown in Figure 5:
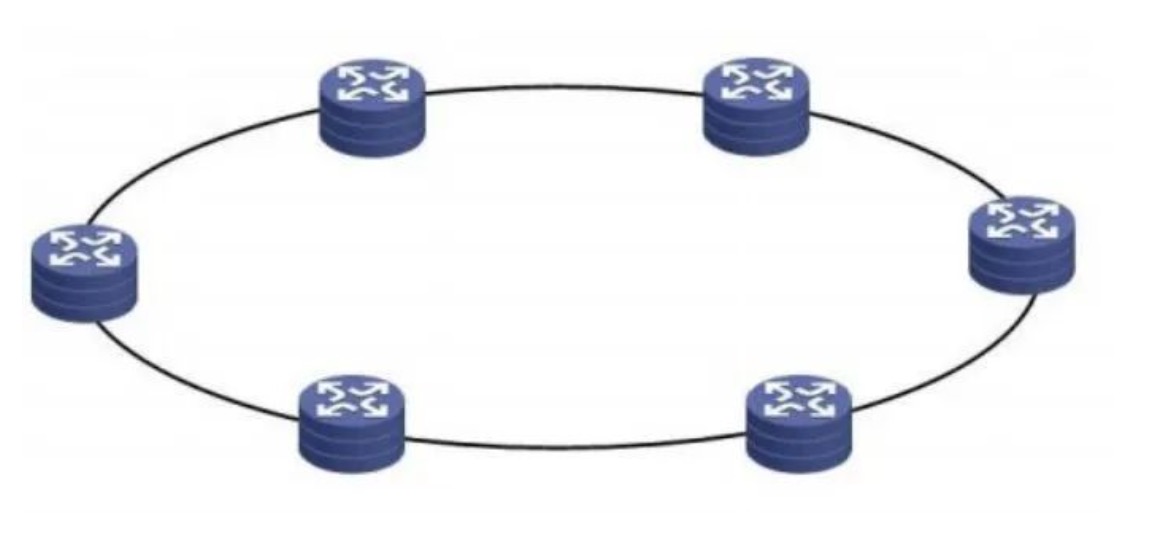
Has the following characteristics:
• Simple topology;
• High bandwidth utilization;
• High reliability. When a fault occurs, it can provide a fault self-healing mechanism for automatic fault protection switching, and the data delay is small. For example, RPR can automatically bypass the traffic to the backup fiber within 50ms when the node fails.
The RPR ring network can add and remove devices without interrupting services. It has good network expansion capabilities in the same ring. However, in terms of cross-ring RRP, complex network topologies such as tangent rings, intersecting rings, and ring-band chains cannot be realized very well, and the ability to independently form large networks is weak.
The above is the news sharing from the PASSHOT. I hope it can be inspired you. If you think today' s content is not too bad, you are welcome to share it with other friends. There are more latest Linux dumps, CCNA 200-301 dumps, CCNP Written dumps and CCIE Written dumps waiting for you.
Cisco Dumps Popular Search:
ccna 4 chapter 1 exam answers ccna updated dumps ccna security certification vs ccnp ccnp switch exam labs ccie dc lab ccie routing and switching lab price spoto dumps feedback is ccna better than network+ ccnp route packet tracer labs ccnp switch pdf kevin wallace
Copyright © 2026 PASSHOT All rights reserved.






