100% Pass Cisco, PMP, CISA, CISM, AWS Dumps on SALE!
Get Now
01:59:56
X
Three minutes to understand the process and classification of QOS
After we briefly understood the basic content of QOS a few days ago, today let us understand the basic processing flow of QOS.
The basic process of QOS is as follows: classification-strategy-identification-queue-scheduling, let us briefly describe.
The first step of QOS must be to classify the data, and the data with the same transmission quality must be one type. Do your best to classify the data according to the default rules. Unified service model and integrated service model: During the data transmission process, the middle node uses the same service model to ensure the transmission of the differentiated service model: between nodes There is no need for signaling interaction. Nodes handle data separately. The strategy has nothing to do with upstream and downstream. It only depends on the local.
QOS classification: Classification is classification, the process is to determine the classification of these packets into various data streams expressed in CoS values according to the trust policy or according to the content of each packet, so the core task of the classification action is to determine Enter the CoS value of the message.
Classification occurs when the port receives incoming packets. When a port is associated with a Policy-map that represents a QoS policy, the classification takes effect on the port, and it applies to all incoming packets from the port.
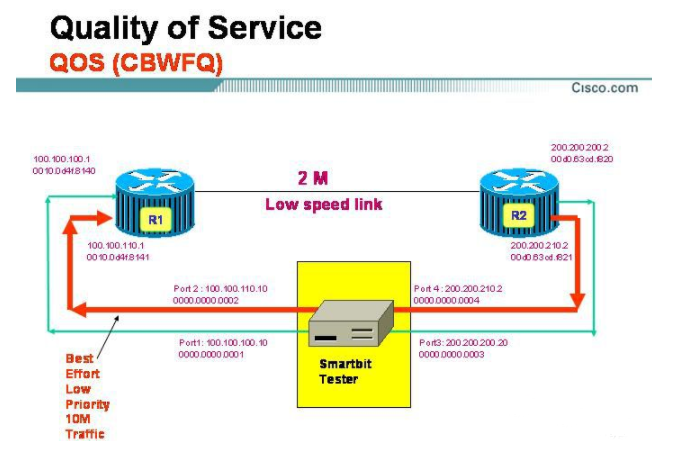
(1) Agreement
Identifying and prioritizing data packets according to the protocol can reduce latency. Applications can be identified by their EtherType.
(2) TCP and UDP port numbers
Many applications use some TCP or UDP ports for communication, such as HTTP using TCP port 80. By checking the port number of the IP packet, the intelligent network can determine which type of application the packet was generated from. This method is also called Layer 4 switching, because both TCP and UDP are on the fourth layer of the OSI model.
(3) Source IP address
Many applications are identified by their source IP address. Because the server is sometimes configured specifically for a single application, such as an email server, analyzing the source IP address of a data packet can identify the application that generated the data packet.
(4) Physical port number
Similar to the source IP address, the physical port number can indicate which server is sending data. This method depends on the mapping relationship between the physical port of the switch and the application server.
The above is the news sharing from the PASSHOT. I hope it can be inspired you. If you think today' s content is not too bad, you are welcome to share it with other friends. There are more latest Linux dumps, CCNA 200-301 dumps, CCNP Written dumps and CCIE Written dumps waiting for you.
Cisco Dumps Popular Search:
free ccna certification how many seats on a boeing 777-200 a ccna exam ccna 200-301 cert guide pdf ccna from scratch 591lab ccnp 200 301 cbt nuggets download ccie security written book rafael ccna dumps ccna 200 301 portable
Copyright © 2026 PASSHOT All rights reserved.






